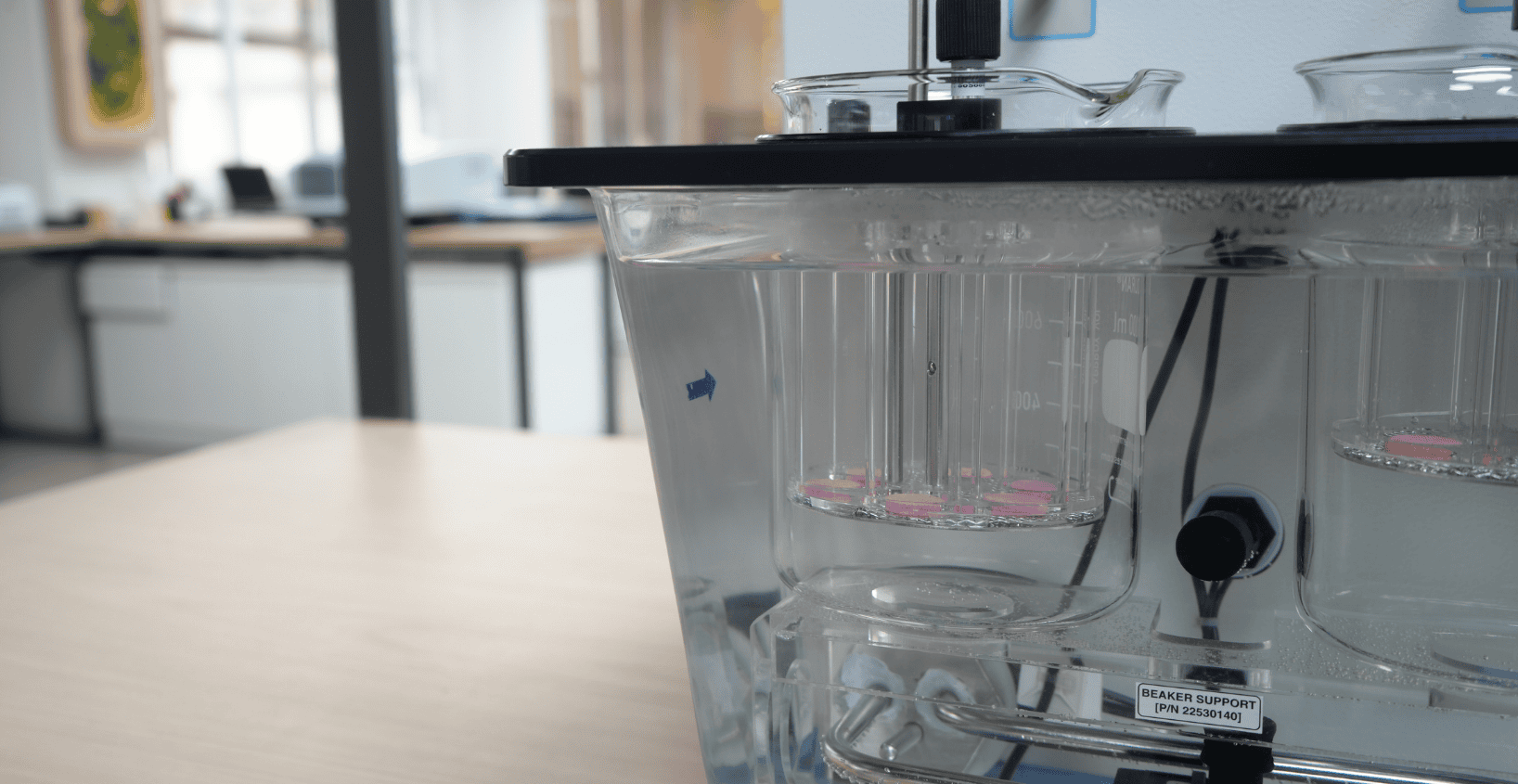
Disintegration Tester
Know more about
Disintegration Tester
The Labindia Tablet Disintegration Tester DT2000S is a user-friendly instrument ideal for entry-level disintegration testing
.png)
1.png)